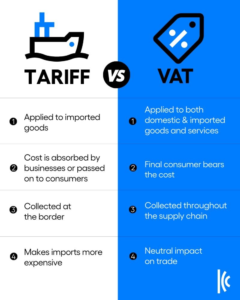
- Distinction Between VAT and Tariffs: The policy brief clarifies that value-added tax (VAT) operates as a consumption tax that is neutral and non-discriminatory, unlike tariffs, which are trade barriers that can favor domestic over foreign businesses.
- Mechanism of VAT: VAT is collected at multiple stages throughout the supply chain, with businesses responsible for collecting and remitting the tax, ultimately passing the cost to the final consumer, ensuring a fair competitive environment for all businesses.
- Principle of VAT Neutrality: VAT is designed to be neutral, taxing goods in the country of consumption rather than production, which prevents it from acting as a trade tariff and ensures that all products in the same market are treated equally regarding tax obligations.
Go directly to Download
Source ccwbo.org